Introduction - Ruby on Rails!
Rails is a server-side web application development framework written in the Ruby programming language. Ruby on Rails help developer to write small to large web applications quickly.
Ruby on Rails is popular among other frameworks because:
- Rails provides amazing tools like scaffolding, which helps in developing web applications in very less time.
- Ruby on Rails is 100% free as it is open source framework.
- It is based on MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern which is popular among web developers.
- RubyGems are the libraries which are available publicly and well documented.
- Ruby is easy to learn.
- Rails supports integrated testing.
- Saves money and time.
- Code can be easily maintained.
- Huge number of helping communities
There are many biggest applications developed from Ruby on Rails like Github, ThemeForest, Groupon, Pixlr, Shopify, Airbnb, etc
Rails Design Principles:
-
MVC (Model, View, Controller)
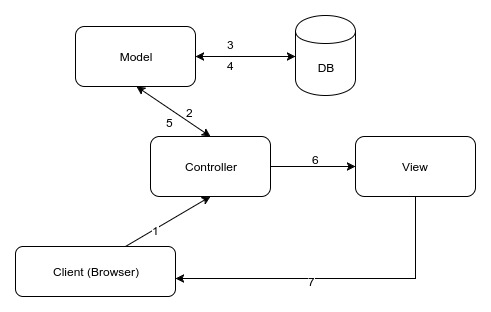
MVC pattern splits an application into three modules a Model, View and Controller. There is “separation of the concerns” among Models, Views and Controllers as each parts has it’s own responsibility.
Model
Model is the layer which interact with the database to retrieve and store the data. You can define the classes in model layer which is used by the application. e.g:
Articlemodel is created when you want to develop article functionality. Model also maintains the relationship between the objects and the database and handles validation, association, transaction, etc.Active Record is the Model in MVC which represents business logic. Business object can be created with the help of Active Record and those object carries persistent data.
View
View layer is the presentation layer which is used to return relevant HTML to be rendered on the users browser. ActionView is the View in Rails MVC which is a part of ActionPack library.
Controller
The controller interacts with the model to retrieve and store data. The retrived data from model will pass to the view. The view returns the resulting HTML to the controller and the controller send this back to the users browser. ActionController is the controller in MVC which handles browser request and acts as channel between Model and View. This is a part of ActionPack library.
-
DRY - Don’t Repeat Yourself
In this principle, developer have to reduce repetition of codes so that code should be more maintainable, more extensible, less buggy.
-
Convention over Configuration
This principle allows developer to use default logics and rules used by the framework so that application can be developed in very less time using very few lines of code. For example:
rails g Articlecommand will create an Article class and articles table unless developer configure another name. So this convention of framework configuration helps in Rapid application development.
Rails Web MVC Architecture