From Server Headaches to Serverless Success: Building APIs That Scale with Lambda and API Gateway
Serverless computing has revolutionized how we build and deploy applications. AWS Lambda, combined with API Gateway, creates a powerful duo that eliminates server management while delivering scalable, cost-effective solutions.
Why Serverless Matters
Gone are the days of provisioning servers, managing infrastructure, or worrying about scaling. With Lambda, you write code, deploy it, and AWS handles everything else. You only pay for what you use - down to the millisecond.
The Perfect Partnership
AWS Lambda executes your code in response to events, while API Gateway acts as the front door, handling HTTP requests and routing them to your Lambda functions. Together, they create REST APIs that can handle thousands of concurrent requests without breaking a sweat.
Real-World Example: Text Analyzer API
I recently built a Ruby-based text analyzer that demonstrates this partnership perfectly:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
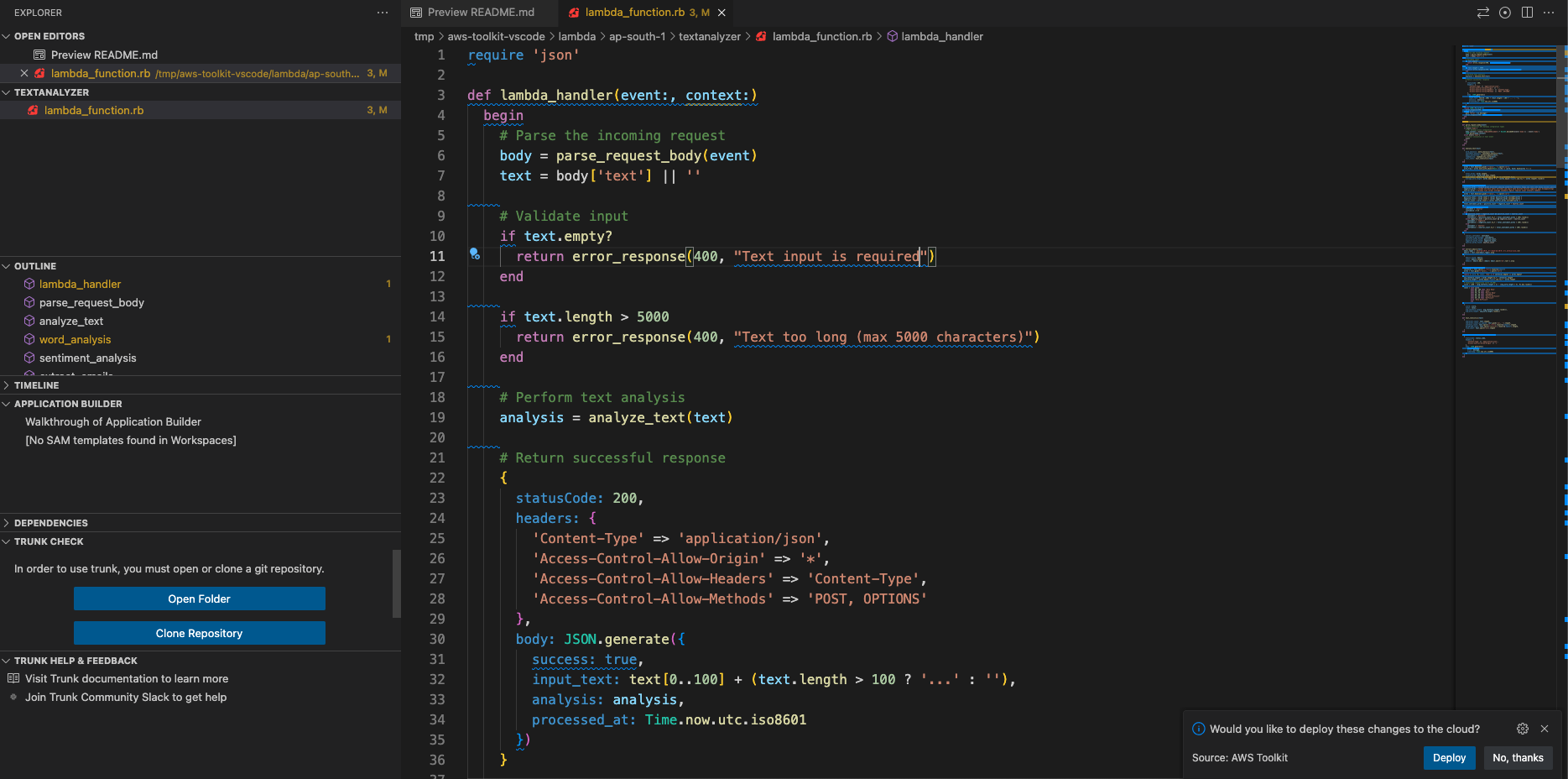
require 'json'
def lambda_handler(event:, context:)
begin
# Parse the incoming request
body = parse_request_body(event)
text = body['text'] || ''
# Validate input
if text.empty?
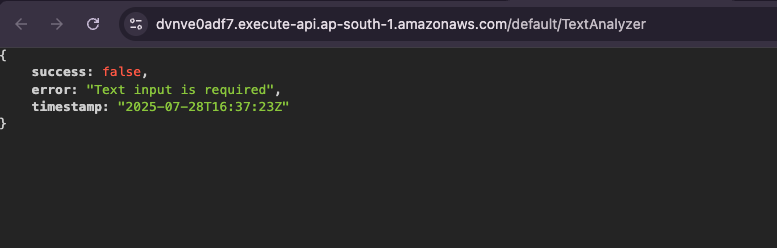
return error_response(400, "Text input is required")
end
if text.length > 5000
return error_response(400, "Text too long (max 5000 characters)")
end
# Perform text analysis
analysis = analyze_text(text)
# Return successful response
{
statusCode: 200,
headers: {
'Content-Type' => 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' => '*',
'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' => 'Content-Type',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' => 'POST, OPTIONS'
},
body: JSON.generate({
success: true,
input_text: text[0..100] + (text.length > 100 ? '...' : ''),
analysis: analysis,
processed_at: Time.now.utc.iso8601
})
}
rescue JSON::ParserError
error_response(400, "Invalid JSON format")
rescue => e
puts "Error: #{e.message}"
error_response(500, "Internal server error")
end
end
private
def parse_request_body(event)
# Handle different API Gateway integration types
if event['body']
# API Gateway proxy integration
body_content = event['isBase64Encoded'] ? Base64.decode64(event['body']) : event['body']
JSON.parse(body_content)
elsif event['text']
# Direct invocation or test event
event
else
{}
end
end
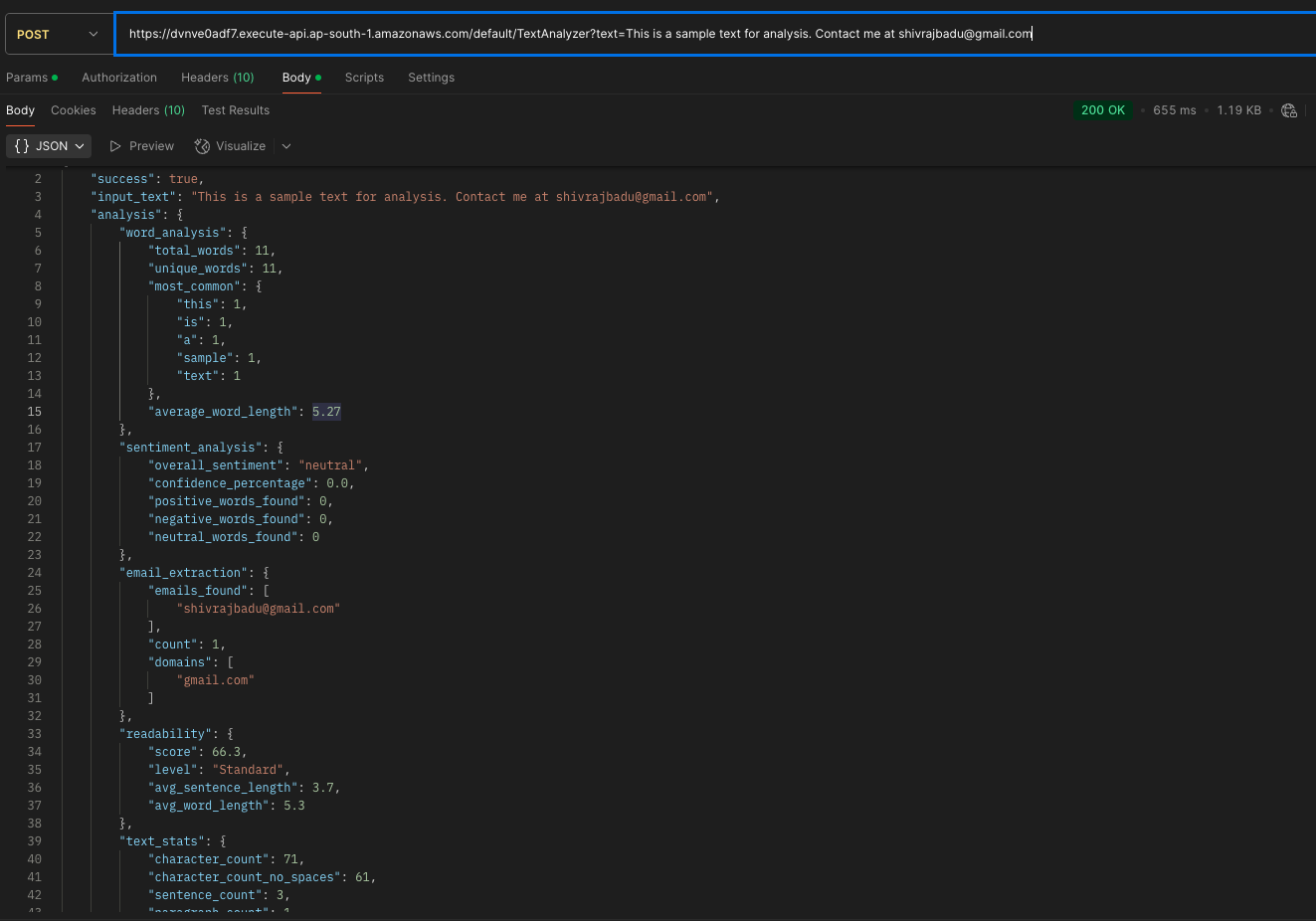
def analyze_text(text)
{
word_analysis: word_analysis(text),
sentiment_analysis: sentiment_analysis(text),
email_extraction: extract_emails(text),
readability: readability_score(text),
text_stats: text_statistics(text)
}
end
def word_analysis(text)
words = text.downcase.gsub(/[^\w\s]/, '').split(/\s+/)
word_freq = words.each_with_object(Hash.new(0)) { |word, hash| hash[word] += 1 }
{
total_words: words.length,
unique_words: word_freq.keys.length,
most_common: word_freq.sort_by { |k, v| -v }.first(5).to_h,
average_word_length: words.empty? ? 0 : (words.map(&:length).sum.to_f / words.length).round(2)
}
end
def sentiment_analysis(text)
positive_words = %w[good great excellent amazing wonderful fantastic happy joy love like enjoy success positive beautiful]
negative_words = %w[bad terrible awful horrible sad angry hate dislike failure negative ugly disappointing]
neutral_words = %w[okay fine normal average standard regular typical usual ordinary common]
words = text.downcase.gsub(/[^\w\s]/, '').split(/\s+/)
positive_count = words.count { |word| positive_words.include?(word) }
negative_count = words.count { |word| negative_words.include?(word) }
neutral_count = words.count { |word| neutral_words.include?(word) }
total_sentiment_words = positive_count + negative_count + neutral_count
if total_sentiment_words == 0
sentiment = 'neutral'
confidence = 0.0
else
if positive_count > negative_count && positive_count > neutral_count
sentiment = 'positive'
confidence = (positive_count.to_f / total_sentiment_words * 100).round(1)
elsif negative_count > positive_count && negative_count > neutral_count
sentiment = 'negative'
confidence = (negative_count.to_f / total_sentiment_words * 100).round(1)
else
sentiment = 'neutral'
confidence = (neutral_count.to_f / total_sentiment_words * 100).round(1)
end
end
{
overall_sentiment: sentiment,
confidence_percentage: confidence,
positive_words_found: positive_count,
negative_words_found: negative_count,
neutral_words_found: neutral_count
}
end
def extract_emails(text)
email_regex = /\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b/
emails = text.scan(email_regex).uniq
{
emails_found: emails,
count: emails.length,
domains: emails.map { |email| email.split('@').last }.uniq
}
end
def readability_score(text)
sentences = text.split(/[.!?]+/).reject(&:empty?)
words = text.gsub(/[^\w\s]/, '').split(/\s+/)
return { score: 0, level: 'N/A' } if sentences.empty? || words.empty?
avg_sentence_length = words.length.to_f / sentences.length
avg_word_length = words.map(&:length).sum.to_f / words.length
# Simplified readability score (0-100)
score = [100 - (avg_sentence_length * 2) - (avg_word_length * 5), 0].max.round(1)
level = case score
when 90..100 then 'Very Easy'
when 80..89 then 'Easy'
when 70..79 then 'Fairly Easy'
when 60..69 then 'Standard'
when 50..59 then 'Fairly Difficult'
when 30..49 then 'Difficult'
else 'Very Difficult'
end
{
score: score,
level: level,
avg_sentence_length: avg_sentence_length.round(1),
avg_word_length: avg_word_length.round(1)
}
end
def text_statistics(text)
{
character_count: text.length,
character_count_no_spaces: text.gsub(/\s/, '').length,
sentence_count: text.split(/[.!?]+/).reject(&:empty?).length,
paragraph_count: text.split(/\n\s*\n/).reject(&:empty?).length,
line_count: text.split(/\n/).length
}
end
def error_response(status_code, message)
{
statusCode: status_code,
headers: {
'Content-Type' => 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' => '*'
},
body: JSON.generate({
success: false,
error: message,
timestamp: Time.now.utc.iso8601
})
}
end
Key Benefits I’ve Experienced
- Zero Infrastructure Management: Deploy and forget
- Automatic Scaling: Handles traffic spikes seamlessly
- Cost Efficiency: Free tier covers 1M requests monthly
- Lightning Fast: Cold starts under 100ms for Ruby functions
- Built-in Monitoring: CloudWatch logs everything
Getting Started is Simple
- Write your function code
- Deploy using Serverless Framework or AWS SAM
- API Gateway automatically creates your endpoints
- Test and iterate rapidly
The serverless paradigm isn’t just a trend - it’s the future of application development. Start small, experiment, and watch your ideas scale effortlessly.
AWS Lambda and API Gateway in Action: A Visual Walkthrough