Simplifying AI Integration in Ruby: Exploring the ruby_llm Gem
Simplifying AI Integration in Ruby: Exploring the ruby_llm Gem
As AI-powered applications become increasingly popular, developers are constantly looking for simple, unified ways to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) into their applications. If you’re a Ruby developer who’s tired of juggling multiple API clients for different AI providers, the ruby_llm gem might be exactly what you’ve been searching for.
What is ruby_llm?
The ruby_llm gem is a unified Ruby interface that allows you to interact with multiple AI providers through a single, consistent API. Instead of learning different SDKs for OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and other providers, you can use one gem to rule them all.
Supported Providers
The gem supports a wide range of AI providers, including:
- OpenAI (GPT-3.5, GPT-4, GPT-4o)
- Anthropic (Claude models)
- Google (Gemini)
- Cohere
- Hugging Face
- Ollama (for local models)
- And many more!
Getting Started
Setting up ruby_llm is refreshingly simple. Add it to your Gemfile:
1
gem 'ruby_llm'
Basic Usage
Here’s how easy it is to get started with the gem:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
require 'ruby_llm'
# Initialize a chat instance
chat = RubyLLM.chat
# Ask more complex questions
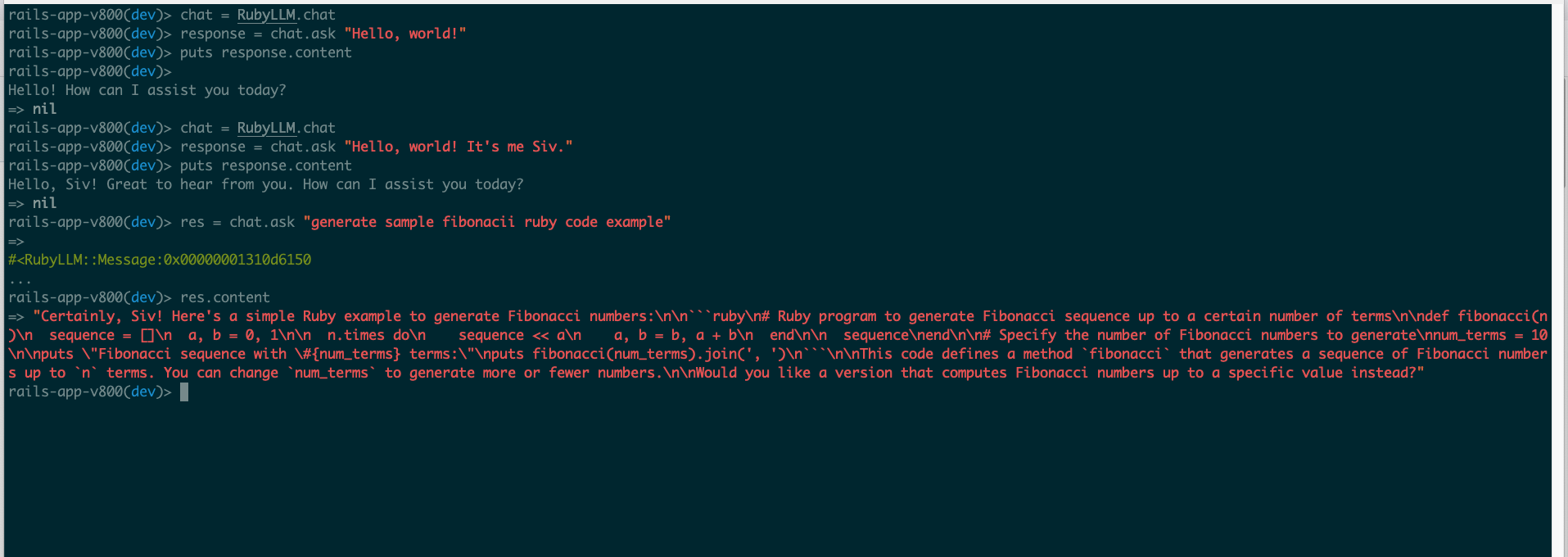
response = chat.ask("Hello, world! It's me Siv.")
puts response.content
# => "Hello, Siv! Great to hear from you. How can I assist you today?"
Advanced Features
Provider Configuration
You can easily switch between different AI providers:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Using OpenAI (default)
chat = RubyLLM.chat(provider: :openai, model: 'gpt-4')
# Using Anthropic's Claude
chat = RubyLLM.chat(provider: :anthropic, model: 'claude-3-sonnet')
# Using Google's Gemini
chat = RubyLLM.chat(provider: :google, model: 'gemini-pro')
Code Generation Example
One of the impressive features I tested was code generation. Here’s an example:
1
2
3
chat = RubyLLM.chat
response = chat.ask("generate sample fibonacci ruby code example")
puts response.content
The gem returned a complete, well-documented Fibonacci implementation:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# Ruby program to generate Fibonacci sequence up to a certain number of terms
def fibonacci(n)
sequence = []
a, b = 0, 1
n.times do
sequence << a
a, b = b, a + b
end
sequence
end
# Specify the number of Fibonacci numbers to generate
num_terms = 10
puts "Fibonacci sequence with #{num_terms} terms:"
puts fibonacci(num_terms).join(', ')
Configuration with Rails
If you’re using Rails, you can easily configure the gem with your API credentials stored in Rails credentials:
Step 1: Add your API key to Rails credentials
1
EDITOR="nano" rails credentials:edit
Add your OpenAI API key:
1
OPENAI_API_KEY: your_api_key_here
Step 2: Configure in an initializer
Create config/initializers/ruby_llm.rb:
1
2
3
4
5
RubyLLM.configure do |config|
config.openai_api_key = Rails.application.credentials.OPENAI_API_KEY
config.anthropic_api_key = Rails.application.credentials.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
# Add other provider keys as needed
end
Real-World Use Cases
1. Content Generation
1
2
chat = RubyLLM.chat
blog_post = chat.ask("Write a technical blog post introduction about Ruby on Rails")
2. Code Review Assistant
1
2
code_to_review = "def calculate(a, b); a + b; end"
review = chat.ask("Review this Ruby code and suggest improvements: #{code_to_review}")
3. Data Analysis Helper
1
2
data_question = "Explain the trends in this CSV data: #{csv_data}"
analysis = chat.ask(data_question)
4. Customer Support Automation
1
2
customer_query = "How do I reset my password?"
support_response = chat.ask("Provide a helpful customer support response: #{customer_query}")
Why Choose ruby_llm?
1. Unified Interface
No need to learn multiple APIs. One consistent interface works across all providers.
2. Easy Provider Switching
Test different models and providers without rewriting your code.
3. Ruby-First Design
Built specifically for Ruby developers, following Ruby conventions and best practices.
4. Minimal Dependencies
Lightweight and doesn’t bloat your application.
5. Production Ready
Handles errors gracefully and includes proper logging.
Best Practices
1. Environment-Specific Configuration
1
2
3
4
5
# config/environments/development.rb
config.ruby_llm_provider = :openai
# config/environments/production.rb
config.ruby_llm_provider = :anthropic
2. Response Handling
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
begin
response = chat.ask("Your question here")
if response.success?
puts response.content
else
puts "Error: #{response.error}"
end
rescue => e
Rails.logger.error "LLM Error: #{e.message}"
end
3. Caching Responses
1
2
3
4
5
6
def cached_ai_response(question)
Rails.cache.fetch("ai_response_#{Digest::MD5.hexdigest(question)}", expires_in: 1.hour) do
chat = RubyLLM.chat
chat.ask(question).content
end
end